Mini-adapton: 用 MoonBit 实现增量计算

介绍
让我们先用一个类似 excel 的例子感受一下增量计算长什么样子. 首先, 定义一个这样的依赖图:
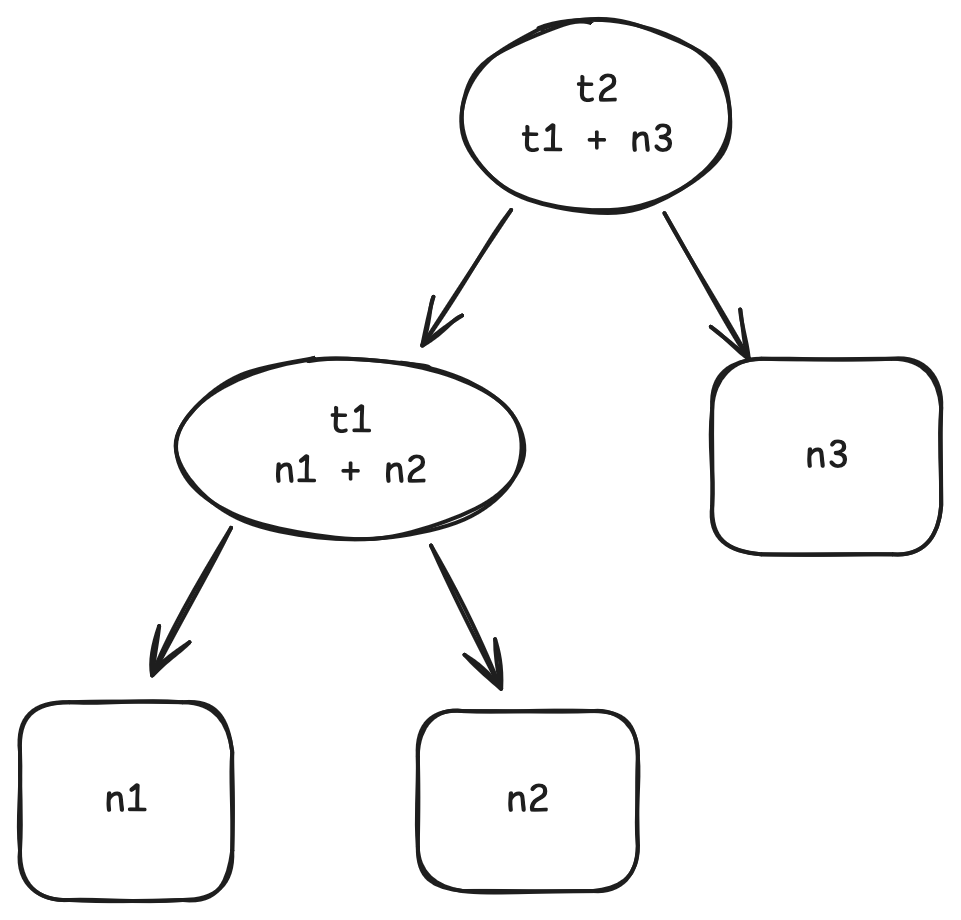
在这个图中, t1 的值通过 n1 + n2 计算得到, t2 的值通过 t1 + n3 计算得到.
当我们想得到 t2 的值时, 该图定义的计算将被执行: 首先通过 n1 + n2 算出 t1, 再通过 t1 + n3 算出 t2. 这个过程和非增量计算是相同的.
但当我们开始改变n1, n2 或 n3 的值时, 事情就不一样了. 比如说我们想将 n1 和 n2 的值互换, 再得到 t2 的值. 在非增量计算中, t1 和 t2 都将被重新计算一遍, 但实际上 t2 是不需要被重新计算的, 因为它依赖的两个值 t1 和 n3 都没有改变 (将 n1 和 n2 的值互换不会改变 t1 的值).
下面的代码实现了我们刚刚举的例子. 我们使用 Cell::new 来定义 n1, n2 和 n3 这些不需要计算的东西, 使用 Thunk::new 来定义 t1 和 t2 这样需要计算的东西.
test {
// a counter to record the times of t2's computation
let mut Int
cnt = 0
// start define the graph
let Cell[Int]
n1 = struct Cell[A] {
mut is_dirty: Bool
mut value: A
mut is_changed: Bool
incoming_edges: Array[&Node]
}
Cell::fn[A : Eq] Cell::new(value : A) -> Cell[A]
new(1)
let Cell[Int]
n2 = struct Cell[A] {
mut is_dirty: Bool
mut value: A
mut is_changed: Bool
incoming_edges: Array[&Node]
}
Cell::fn[A : Eq] Cell::new(value : A) -> Cell[A]
new(2)
let Cell[Int]
n3 = struct Cell[A] {
mut is_dirty: Bool
mut value: A
mut is_changed: Bool
incoming_edges: Array[&Node]
}
Cell::fn[A : Eq] Cell::new(value : A) -> Cell[A]
new(3)
let Thunk[Int]
t1 = struct Thunk[A] {
mut is_dirty: Bool
mut value: A?
mut is_changed: Bool
thunk: () -> A
incoming_edges: Array[&Node]
outgoing_edges: Array[&Node]
}
Thunk::fn[A : Eq] Thunk::new(thunk : () -> A) -> Thunk[A]
new(fn() {
Cell[Int]
n1.fn[A] Cell::get(self : Cell[A]) -> A
get() fn Add::add(self : Int, other : Int) -> Int
Adds two 32-bit signed integers. Performs two's complement arithmetic, which
means the operation will wrap around if the result exceeds the range of a
32-bit integer.
Parameters:
self : The first integer operand.other : The second integer operand.
Returns a new integer that is the sum of the two operands. If the
mathematical sum exceeds the range of a 32-bit integer (-2,147,483,648 to
2,147,483,647), the result wraps around according to two's complement rules.
Example:
test {
inspect(42 + 1, content="43")
inspect(2147483647 + 1, content="-2147483648") // Overflow wraps around to minimum value
}
+ Cell[Int]
n2.fn[A] Cell::get(self : Cell[A]) -> A
get()
})
let Thunk[Int]
t2 = struct Thunk[A] {
mut is_dirty: Bool
mut value: A?
mut is_changed: Bool
thunk: () -> A
incoming_edges: Array[&Node]
outgoing_edges: Array[&Node]
}
Thunk::fn[A : Eq] Thunk::new(thunk : () -> A) -> Thunk[A]
new(fn() {
Int
cnt fn Add::add(self : Int, other : Int) -> Int
Adds two 32-bit signed integers. Performs two's complement arithmetic, which
means the operation will wrap around if the result exceeds the range of a
32-bit integer.
Parameters:
self : The first integer operand.other : The second integer operand.
Returns a new integer that is the sum of the two operands. If the
mathematical sum exceeds the range of a 32-bit integer (-2,147,483,648 to
2,147,483,647), the result wraps around according to two's complement rules.
Example:
test {
inspect(42 + 1, content="43")
inspect(2147483647 + 1, content="-2147483648") // Overflow wraps around to minimum value
}
+= 1
Thunk[Int]
t1.fn[A : Eq] Thunk::get(self : Thunk[A]) -> A
get() fn Add::add(self : Int, other : Int) -> Int
Adds two 32-bit signed integers. Performs two's complement arithmetic, which
means the operation will wrap around if the result exceeds the range of a
32-bit integer.
Parameters:
self : The first integer operand.other : The second integer operand.
Returns a new integer that is the sum of the two operands. If the
mathematical sum exceeds the range of a 32-bit integer (-2,147,483,648 to
2,147,483,647), the result wraps around according to two's complement rules.
Example:
test {
inspect(42 + 1, content="43")
inspect(2147483647 + 1, content="-2147483648") // Overflow wraps around to minimum value
}
+ Cell[Int]
n3.fn[A] Cell::get(self : Cell[A]) -> A
get()
})
// get the value of t2
fn inspect(obj : &Show, content~ : String, loc~ : SourceLoc = _, args_loc~ : ArgsLoc = _) -> Unit raise InspectError
Tests if the string representation of an object matches the expected content.
Used primarily in test cases to verify the correctness of Show
implementations and program outputs.
Parameters:
object : The object to be inspected. Must implement the Show trait.content : The expected string representation of the object. Defaults to
an empty string.location : Source code location information for error reporting.
Automatically provided by the compiler.arguments_location : Location information for function arguments in
source code. Automatically provided by the compiler.
Throws an InspectError if the actual string representation of the object
does not match the expected content. The error message includes detailed
information about the mismatch, including source location and both expected
and actual values.
Example:
test {
inspect(42, content="42")
inspect("hello", content="hello")
inspect([1, 2, 3], content="[1, 2, 3]")
}
inspect(Thunk[Int]
t2.fn[A : Eq] Thunk::get(self : Thunk[A]) -> A
get(), String
content="6")
fn inspect(obj : &Show, content~ : String, loc~ : SourceLoc = _, args_loc~ : ArgsLoc = _) -> Unit raise InspectError
Tests if the string representation of an object matches the expected content.
Used primarily in test cases to verify the correctness of Show
implementations and program outputs.
Parameters:
object : The object to be inspected. Must implement the Show trait.content : The expected string representation of the object. Defaults to
an empty string.location : Source code location information for error reporting.
Automatically provided by the compiler.arguments_location : Location information for function arguments in
source code. Automatically provided by the compiler.
Throws an InspectError if the actual string representation of the object
does not match the expected content. The error message includes detailed
information about the mismatch, including source location and both expected
and actual values.
Example:
test {
inspect(42, content="42")
inspect("hello", content="hello")
inspect([1, 2, 3], content="[1, 2, 3]")
}
inspect(Int
cnt, String
content="1")
// swap value of n1 and n2
Cell[Int]
n1.fn[A : Eq] Cell::set(self : Cell[A], new_value : A) -> Unit
set(2)
Cell[Int]
n2.fn[A : Eq] Cell::set(self : Cell[A], new_value : A) -> Unit
set(1)
fn inspect(obj : &Show, content~ : String, loc~ : SourceLoc = _, args_loc~ : ArgsLoc = _) -> Unit raise InspectError
Tests if the string representation of an object matches the expected content.
Used primarily in test cases to verify the correctness of Show
implementations and program outputs.
Parameters:
object : The object to be inspected. Must implement the Show trait.content : The expected string representation of the object. Defaults to
an empty string.location : Source code location information for error reporting.
Automatically provided by the compiler.arguments_location : Location information for function arguments in
source code. Automatically provided by the compiler.
Throws an InspectError if the actual string representation of the object
does not match the expected content. The error message includes detailed
information about the mismatch, including source location and both expected
and actual values.
Example:
test {
inspect(42, content="42")
inspect("hello", content="hello")
inspect([1, 2, 3], content="[1, 2, 3]")
}
inspect(Thunk[Int]
t2.fn[A : Eq] Thunk::get(self : Thunk[A]) -> A
get(), String
content="6")
// t2 does not recompute
fn inspect(obj : &Show, content~ : String, loc~ : SourceLoc = _, args_loc~ : ArgsLoc = _) -> Unit raise InspectError
Tests if the string representation of an object matches the expected content.
Used primarily in test cases to verify the correctness of Show
implementations and program outputs.
Parameters:
object : The object to be inspected. Must implement the Show trait.content : The expected string representation of the object. Defaults to
an empty string.location : Source code location information for error reporting.
Automatically provided by the compiler.arguments_location : Location information for function arguments in
source code. Automatically provided by the compiler.
Throws an InspectError if the actual string representation of the object
does not match the expected content. The error message includes detailed
information about the mismatch, including source location and both expected
and actual values.
Example:
test {
inspect(42, content="42")
inspect("hello", content="hello")
inspect([1, 2, 3], content="[1, 2, 3]")
}
inspect(Int
cnt, String
content="1")
}
在这篇文章中, 我们将介绍如何在 MoonBit 中实现一个增量计算库. 这个库的 API 就是我们上面例子中出现的那些:
Cell::new
Cell::get
Cell::set
Thunk::new
Thunk::get
问题分析和解法
要实现这个库, 我们主要有三个问题需要解决:
如何在运行时构建依赖图
作为一个使用 MoonBit 实现的库, 没有简单方法让我们可以静态地构建依赖图, 因为 MoonBit 目前还不支持任何元编程的机制. 因此我们需要动态地把依赖图构建出来. 事实上, 我们关心的只是哪些 thunk 或 cell 被另一个 thunk 依赖了, 所以一个不错的构建依赖图的时机就是在用户调用 Thunk::get 的时候. 比如在上面的例子中:
let n1 = Cell::new(1)
let n2 = Cell::new(2)
let n3 = Cell::new(3)
let t1 = Thunk::new(fn() { n1.get() + n2.get() })
let t2 = Thunk::new(fn() { t1.get() + n3.get() })
t2.get()
当用户调用 t2.get() 时, 我们在运行时会知道 t1.get() 和 n3.get() 在其中也被调用了. 因此 t1 和 n3 是 t2 的依赖, 并且我们可以构建一个这样的图:
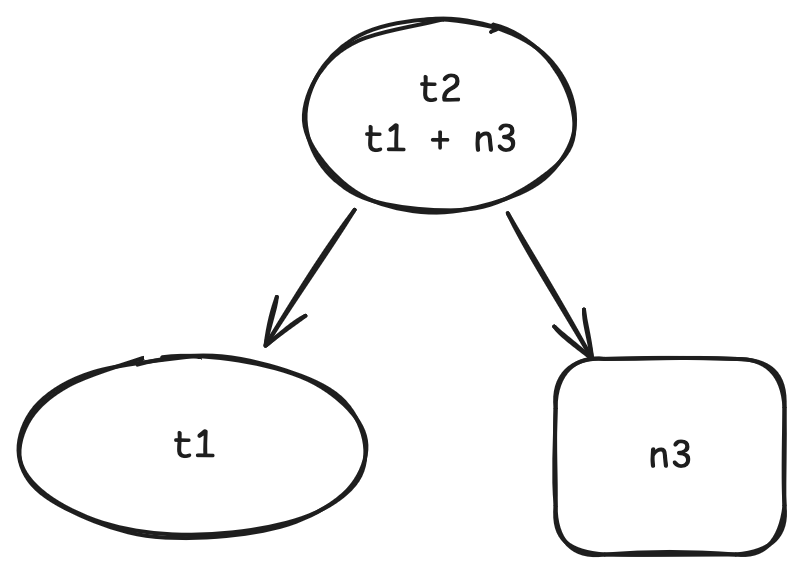
同样的过程也会在 t1.get() 被调用时发生.
所以计划是这样的:
- 我们定义一个栈来记录我们当前在获得哪个 thunk 的值. 在这里使用栈的原因是, 我们事实上是在尝试记录每个
get的调用栈. - 当我们调用
get时, 将其标记为栈顶 thunk 的依赖, 如果它是一个 thunk, 再把它压栈. - 当一个 thunk 的
get结束时, 将它出栈.
让我们看看上面那个例子在这个算法下的过程是什么样子的:
-
当我们调用
t2.get时, 将t2压栈.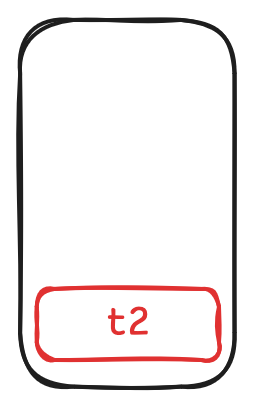
-
当我们在
t2.get中调用t1.get时, 将t1记为t2的依赖, 并将t1压栈.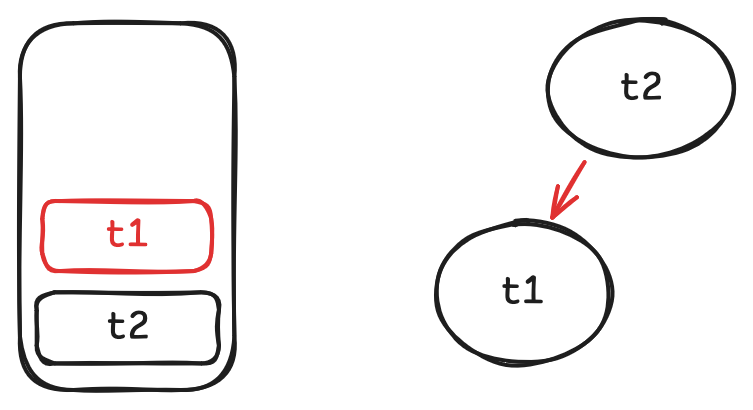
-
当我们在
t1.get中调用n1.get时, 将 n1 记为t1的依赖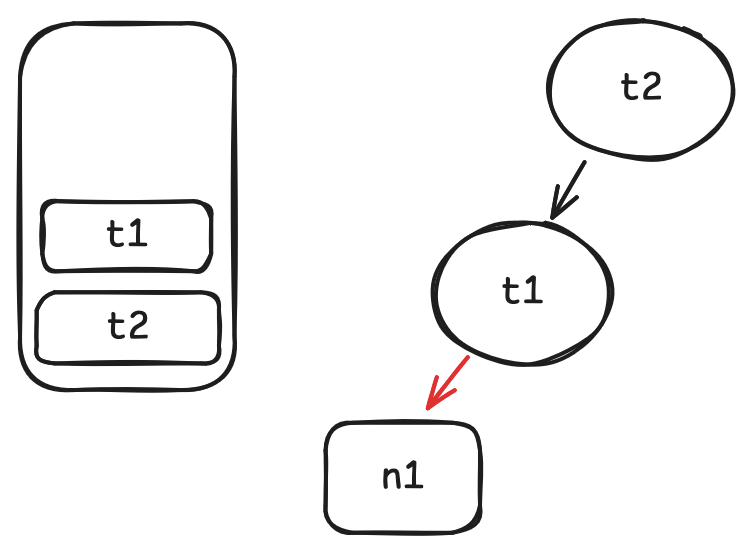
-
相同的过程发生在
n2身上.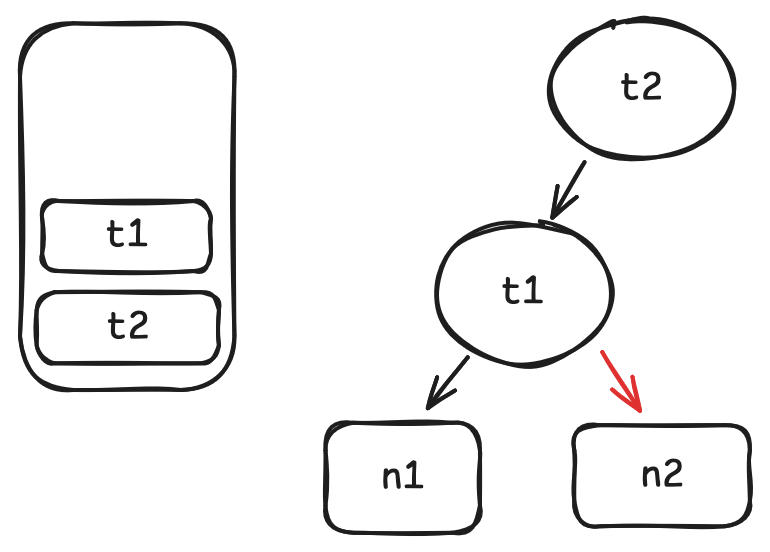
-
当
t1.get结束时, 将t1出栈.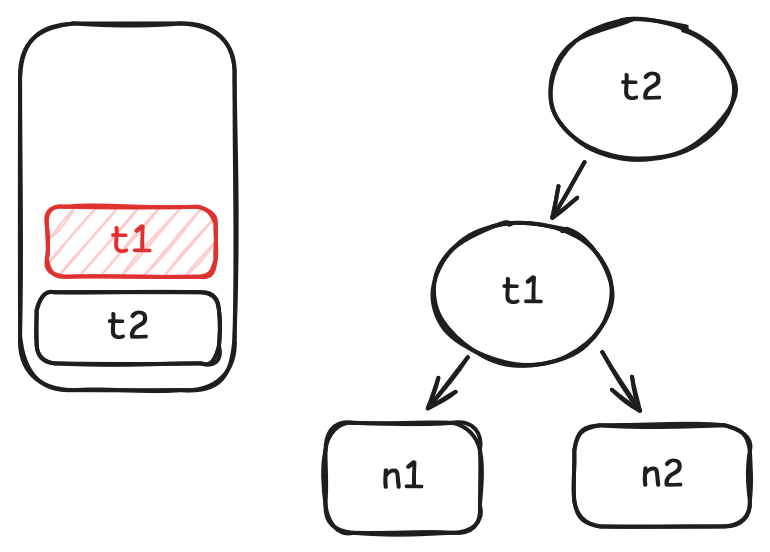
-
当我们调用
n3.get时, 将n3记为t2的依赖.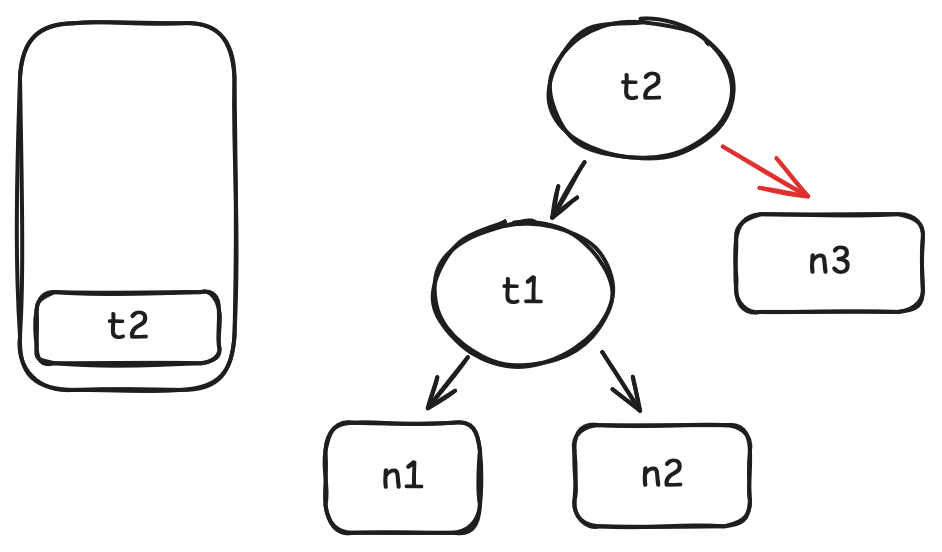
除了这些从父依赖到子依赖的边之外, 我们最好也记录一个从子依赖到父依赖的边, 方便后面我们在这个图上反向便利.
在接下来的代码中, 我们将使用 outgoing_edges 指代从父依赖到子依赖的边, 使用 incoming_edges 指代中子依赖到父依赖的边.
如何标记过时的节点
当我们调用 Cell::set 时, 该节点本身和所有依赖它的节点都应该被标记为过时的. 这将在后面作为判断一个 thunk 是否需要重新计算的标准之一. 这基本上是一个从图的叶子节点向后遍历的过程. 我们可以用这样的伪 MoonBit 代码表示这个算法:
fn dirty(node: Node) -> Unit {
for n in node.incoming_edges {
n.set_dirty(true)
dirty(node)
}
}
如何决定一个 thunk 需要被重新计算
当我们调用 Thunk::get 时, 我们需要决定是否它需要被重新计算. 但只用我们在上一节描述的方法是不够的. 如果我们只使用是否过时这一个标准进行判断, 势必会有不需要的计算发生. 比如我们在一开始给出的例子:
n1.set(2)
n2.set(1)
inspect(t2.get(), content="6")
当我们调换 n1 和 n2 的值时, n1, n2, t1 和 t2 都应该被标记为过时, 但当我们调用 t2.get 时, 其实没有必要重新计算 t2, 因为 t1 的值并没有改变.
这提醒我们除了过时之外, 我们还要考虑依赖的值是否和它上一次的值一样. 如果一个节点既是过时的, 并且它的依赖中存在一个值和上一次不同, 那么它应该被重新计算.
我们可以用下面的伪 MoonBit 代码描述这个算法:
fn propagate(self: Node) -> Unit {
// 当一个节点过时了, 它可能需要被重新计算
if self.is_dirty() {
// 重新计算之后, 它将不在是过时的
self.set_dirty(false)
for dependency in self.outgoing_edges() {
// 递归地重新计算每个依赖
dependency.propagate()
// 如果一个依赖的值改变了, 这个节点需要被重新计算
if dependency.is_changed() {
// 移除所有的 outgoing_edges, 它们将在被计算时重新构建
self.outgoing_edges().clear()
self.evaluate()
return
}
}
}
}
实现
基于上面描述的代码, 实现是比较直观的.
首先, 我们先定义 Cell:
struct Cell[A] {
mut Bool
is_dirty : Bool
Bool
mut A
value : type parameter A
A
mut Bool
is_changed : Bool
Bool
Array[&Node]
incoming_edges : type Array[T]
An Array is a collection of values that supports random access and can
grow in size.
Array[&trait Node {
is_dirty(Self) -> Bool
set_dirty(Self, Bool) -> Unit
incoming_edges(Self) -> Array[&Node]
outgoing_edges(Self) -> Array[&Node]
is_changed(Self) -> Bool
evaluate(Self) -> Unit
}
Node]
}
由于 Cell 只会是依赖图中的叶子节点, 所以它没有 outgoing_edges. 这里出现的特征 Node 是用来抽象依赖图中的节点的.
接着, 我们定义 Thunk:
struct Thunk[A] {
mut Bool
is_dirty : Bool
Bool
mut A?
value : type parameter A
A?
mut Bool
is_changed : Bool
Bool
() -> A
thunk : () -> type parameter A
A
Array[&Node]
incoming_edges : type Array[T]
An Array is a collection of values that supports random access and can
grow in size.
Array[&trait Node {
is_dirty(Self) -> Bool
set_dirty(Self, Bool) -> Unit
incoming_edges(Self) -> Array[&Node]
outgoing_edges(Self) -> Array[&Node]
is_changed(Self) -> Bool
evaluate(Self) -> Unit
}
Node]
Array[&Node]
outgoing_edges : type Array[T]
An Array is a collection of values that supports random access and can
grow in size.
Array[&trait Node {
is_dirty(Self) -> Bool
set_dirty(Self, Bool) -> Unit
incoming_edges(Self) -> Array[&Node]
outgoing_edges(Self) -> Array[&Node]
is_changed(Self) -> Bool
evaluate(Self) -> Unit
}
Node]
}
Thunk 的值是可选的, 因为它只有在我们第一次调用 Thunk::get 之后才会存在.
我们可以很简单地给这两个类型实现 new:
fn[A : trait Eq {
equal(Self, Self) -> Bool
op_equal(Self, Self) -> Bool
not_equal(Self, Self) -> Bool
}
Trait for types whose elements can test for equality
Eq] struct Cell[A] {
mut is_dirty: Bool
mut value: A
mut is_changed: Bool
incoming_edges: Array[&Node]
}
Cell::fn[A : Eq] Cell::new(value : A) -> Cell[A]
new(A
value : type parameter A
A) -> struct Cell[A] {
mut is_dirty: Bool
mut value: A
mut is_changed: Bool
incoming_edges: Array[&Node]
}
Cell[type parameter A
A] {
struct Cell[A] {
mut is_dirty: Bool
mut value: A
mut is_changed: Bool
incoming_edges: Array[&Node]
}
Cell::{
Bool
is_changed: false,
A
value,
Array[&Node]
incoming_edges: [],
Bool
is_dirty: false,
}
}
fn[A : trait Eq {
equal(Self, Self) -> Bool
op_equal(Self, Self) -> Bool
not_equal(Self, Self) -> Bool
}
Trait for types whose elements can test for equality
Eq] struct Thunk[A] {
mut is_dirty: Bool
mut value: A?
mut is_changed: Bool
thunk: () -> A
incoming_edges: Array[&Node]
outgoing_edges: Array[&Node]
}
Thunk::fn[A : Eq] Thunk::new(thunk : () -> A) -> Thunk[A]
new(() -> A
thunk : () -> type parameter A
A) -> struct Thunk[A] {
mut is_dirty: Bool
mut value: A?
mut is_changed: Bool
thunk: () -> A
incoming_edges: Array[&Node]
outgoing_edges: Array[&Node]
}
Thunk[type parameter A
A] {
struct Thunk[A] {
mut is_dirty: Bool
mut value: A?
mut is_changed: Bool
thunk: () -> A
incoming_edges: Array[&Node]
outgoing_edges: Array[&Node]
}
Thunk::{
A?
value: A?
None,
Bool
is_changed: false,
() -> A
thunk,
Array[&Node]
incoming_edges: [],
Array[&Node]
outgoing_edges: [],
Bool
is_dirty: false,
}
}
Thunk 和 Cell 是依赖图的两种节点, 我们可以使用一个特征 Node 来抽象它们:
trait trait Node {
is_dirty(Self) -> Bool
set_dirty(Self, Bool) -> Unit
incoming_edges(Self) -> Array[&Node]
outgoing_edges(Self) -> Array[&Node]
is_changed(Self) -> Bool
evaluate(Self) -> Unit
}
Node {
(Self) -> Bool
is_dirty(type parameter Self
Self) -> Bool
Bool
(Self, Bool) -> Unit
set_dirty(type parameter Self
Self, Bool
Bool) -> Unit
Unit
(Self) -> Array[&Node]
incoming_edges(type parameter Self
Self) -> type Array[T]
An Array is a collection of values that supports random access and can
grow in size.
Array[&trait Node {
is_dirty(Self) -> Bool
set_dirty(Self, Bool) -> Unit
incoming_edges(Self) -> Array[&Node]
outgoing_edges(Self) -> Array[&Node]
is_changed(Self) -> Bool
evaluate(Self) -> Unit
}
Node]
(Self) -> Array[&Node]
outgoing_edges(type parameter Self
Self) -> type Array[T]
An Array is a collection of values that supports random access and can
grow in size.
Array[&trait Node {
is_dirty(Self) -> Bool
set_dirty(Self, Bool) -> Unit
incoming_edges(Self) -> Array[&Node]
outgoing_edges(Self) -> Array[&Node]
is_changed(Self) -> Bool
evaluate(Self) -> Unit
}
Node]
(Self) -> Bool
is_changed(type parameter Self
Self) -> Bool
Bool
(Self) -> Unit
evaluate(type parameter Self
Self) -> Unit
Unit
}
为两个类型实现这个特征:
impl[A] trait Node {
is_dirty(Self) -> Bool
set_dirty(Self, Bool) -> Unit
incoming_edges(Self) -> Array[&Node]
outgoing_edges(Self) -> Array[&Node]
is_changed(Self) -> Bool
evaluate(Self) -> Unit
}
Node for struct Cell[A] {
mut is_dirty: Bool
mut value: A
mut is_changed: Bool
incoming_edges: Array[&Node]
}
Cell[type parameter A
A] with fn[A] Node::incoming_edges(self : Cell[A]) -> Array[&Node]
incoming_edges(Cell[A]
self) {
Cell[A]
self.Array[&Node]
incoming_edges
}
impl[A] trait Node {
is_dirty(Self) -> Bool
set_dirty(Self, Bool) -> Unit
incoming_edges(Self) -> Array[&Node]
outgoing_edges(Self) -> Array[&Node]
is_changed(Self) -> Bool
evaluate(Self) -> Unit
}
Node for struct Cell[A] {
mut is_dirty: Bool
mut value: A
mut is_changed: Bool
incoming_edges: Array[&Node]
}
Cell[type parameter A
A] with fn[A] Node::outgoing_edges(_self : Cell[A]) -> Array[&Node]
outgoing_edges(Cell[A]
_self) {
[]
}
impl[A] trait Node {
is_dirty(Self) -> Bool
set_dirty(Self, Bool) -> Unit
incoming_edges(Self) -> Array[&Node]
outgoing_edges(Self) -> Array[&Node]
is_changed(Self) -> Bool
evaluate(Self) -> Unit
}
Node for struct Cell[A] {
mut is_dirty: Bool
mut value: A
mut is_changed: Bool
incoming_edges: Array[&Node]
}
Cell[type parameter A
A] with fn[A] Node::is_dirty(self : Cell[A]) -> Bool
is_dirty(Cell[A]
self) {
Cell[A]
self.Bool
is_dirty
}
impl[A] trait Node {
is_dirty(Self) -> Bool
set_dirty(Self, Bool) -> Unit
incoming_edges(Self) -> Array[&Node]
outgoing_edges(Self) -> Array[&Node]
is_changed(Self) -> Bool
evaluate(Self) -> Unit
}
Node for struct Cell[A] {
mut is_dirty: Bool
mut value: A
mut is_changed: Bool
incoming_edges: Array[&Node]
}
Cell[type parameter A
A] with fn[A] Node::set_dirty(self : Cell[A], new_dirty : Bool) -> Unit
set_dirty(Cell[A]
self, Bool
new_dirty) {
Cell[A]
self.Bool
is_dirty = Bool
new_dirty
}
impl[A] trait Node {
is_dirty(Self) -> Bool
set_dirty(Self, Bool) -> Unit
incoming_edges(Self) -> Array[&Node]
outgoing_edges(Self) -> Array[&Node]
is_changed(Self) -> Bool
evaluate(Self) -> Unit
}
Node for struct Cell[A] {
mut is_dirty: Bool
mut value: A
mut is_changed: Bool
incoming_edges: Array[&Node]
}
Cell[type parameter A
A] with fn[A] Node::is_changed(self : Cell[A]) -> Bool
is_changed(Cell[A]
self) {
Cell[A]
self.Bool
is_changed
}
impl[A] trait Node {
is_dirty(Self) -> Bool
set_dirty(Self, Bool) -> Unit
incoming_edges(Self) -> Array[&Node]
outgoing_edges(Self) -> Array[&Node]
is_changed(Self) -> Bool
evaluate(Self) -> Unit
}
Node for struct Cell[A] {
mut is_dirty: Bool
mut value: A
mut is_changed: Bool
incoming_edges: Array[&Node]
}
Cell[type parameter A
A] with fn[A] Node::evaluate(_self : Cell[A]) -> Unit
evaluate(Cell[A]
_self) {
()
}
impl[A : trait Eq {
equal(Self, Self) -> Bool
op_equal(Self, Self) -> Bool
not_equal(Self, Self) -> Bool
}
Trait for types whose elements can test for equality
Eq] trait Node {
is_dirty(Self) -> Bool
set_dirty(Self, Bool) -> Unit
incoming_edges(Self) -> Array[&Node]
outgoing_edges(Self) -> Array[&Node]
is_changed(Self) -> Bool
evaluate(Self) -> Unit
}
Node for struct Thunk[A] {
mut is_dirty: Bool
mut value: A?
mut is_changed: Bool
thunk: () -> A
incoming_edges: Array[&Node]
outgoing_edges: Array[&Node]
}
Thunk[type parameter A
A] with fn[A : Eq] Node::is_changed(self : Thunk[A]) -> Bool
is_changed(Thunk[A]
self) {
Thunk[A]
self.Bool
is_changed
}
impl[A : trait Eq {
equal(Self, Self) -> Bool
op_equal(Self, Self) -> Bool
not_equal(Self, Self) -> Bool
}
Trait for types whose elements can test for equality
Eq] trait Node {
is_dirty(Self) -> Bool
set_dirty(Self, Bool) -> Unit
incoming_edges(Self) -> Array[&Node]
outgoing_edges(Self) -> Array[&Node]
is_changed(Self) -> Bool
evaluate(Self) -> Unit
}
Node for struct Thunk[A] {
mut is_dirty: Bool
mut value: A?
mut is_changed: Bool
thunk: () -> A
incoming_edges: Array[&Node]
outgoing_edges: Array[&Node]
}
Thunk[type parameter A
A] with fn[A : Eq] Node::outgoing_edges(self : Thunk[A]) -> Array[&Node]
outgoing_edges(Thunk[A]
self) {
Thunk[A]
self.Array[&Node]
outgoing_edges
}
impl[A : trait Eq {
equal(Self, Self) -> Bool
op_equal(Self, Self) -> Bool
not_equal(Self, Self) -> Bool
}
Trait for types whose elements can test for equality
Eq] trait Node {
is_dirty(Self) -> Bool
set_dirty(Self, Bool) -> Unit
incoming_edges(Self) -> Array[&Node]
outgoing_edges(Self) -> Array[&Node]
is_changed(Self) -> Bool
evaluate(Self) -> Unit
}
Node for struct Thunk[A] {
mut is_dirty: Bool
mut value: A?
mut is_changed: Bool
thunk: () -> A
incoming_edges: Array[&Node]
outgoing_edges: Array[&Node]
}
Thunk[type parameter A
A] with fn[A : Eq] Node::incoming_edges(self : Thunk[A]) -> Array[&Node]
incoming_edges(Thunk[A]
self) {
Thunk[A]
self.Array[&Node]
incoming_edges
}
impl[A : trait Eq {
equal(Self, Self) -> Bool
op_equal(Self, Self) -> Bool
not_equal(Self, Self) -> Bool
}
Trait for types whose elements can test for equality
Eq] trait Node {
is_dirty(Self) -> Bool
set_dirty(Self, Bool) -> Unit
incoming_edges(Self) -> Array[&Node]
outgoing_edges(Self) -> Array[&Node]
is_changed(Self) -> Bool
evaluate(Self) -> Unit
}
Node for struct Thunk[A] {
mut is_dirty: Bool
mut value: A?
mut is_changed: Bool
thunk: () -> A
incoming_edges: Array[&Node]
outgoing_edges: Array[&Node]
}
Thunk[type parameter A
A] with fn[A : Eq] Node::is_dirty(self : Thunk[A]) -> Bool
is_dirty(Thunk[A]
self) {
Thunk[A]
self.Bool
is_dirty
}
impl[A : trait Eq {
equal(Self, Self) -> Bool
op_equal(Self, Self) -> Bool
not_equal(Self, Self) -> Bool
}
Trait for types whose elements can test for equality
Eq] trait Node {
is_dirty(Self) -> Bool
set_dirty(Self, Bool) -> Unit
incoming_edges(Self) -> Array[&Node]
outgoing_edges(Self) -> Array[&Node]
is_changed(Self) -> Bool
evaluate(Self) -> Unit
}
Node for struct Thunk[A] {
mut is_dirty: Bool
mut value: A?
mut is_changed: Bool
thunk: () -> A
incoming_edges: Array[&Node]
outgoing_edges: Array[&Node]
}
Thunk[type parameter A
A] with fn[A : Eq] Node::set_dirty(self : Thunk[A], new_dirty : Bool) -> Unit
set_dirty(Thunk[A]
self, Bool
new_dirty) {
Thunk[A]
self.Bool
is_dirty = Bool
new_dirty
}
impl[A : trait Eq {
equal(Self, Self) -> Bool
op_equal(Self, Self) -> Bool
not_equal(Self, Self) -> Bool
}
Trait for types whose elements can test for equality
Eq] trait Node {
is_dirty(Self) -> Bool
set_dirty(Self, Bool) -> Unit
incoming_edges(Self) -> Array[&Node]
outgoing_edges(Self) -> Array[&Node]
is_changed(Self) -> Bool
evaluate(Self) -> Unit
}
Node for struct Thunk[A] {
mut is_dirty: Bool
mut value: A?
mut is_changed: Bool
thunk: () -> A
incoming_edges: Array[&Node]
outgoing_edges: Array[&Node]
}
Thunk[type parameter A
A] with fn[A : Eq] Node::evaluate(self : Thunk[A]) -> Unit
evaluate(Thunk[A]
self) {
let node_stack : Array[&Node]
node_stack.fn[T] Array::push(self : Array[T], value : T) -> Unit
Adds an element to the end of the array.
If the array is at capacity, it will be reallocated.
Example
test {
let v = []
v.push(3)
}
push(Thunk[A]
self)
let A
value = (Thunk[A]
self.() -> A
thunk)()
Thunk[A]
self.Bool
is_changed = match Thunk[A]
self.A?
value {
A?
None => true
(A) -> A?
Some(A
v) => A
v (_ : A, _ : A) -> Bool
!= A
value
}
Thunk[A]
self.A?
value = (A) -> A?
Some(A
value)
let node_stack : Array[&Node]
node_stack.fn[T] Array::unsafe_pop(self : Array[T]) -> T
Removes and returns the last element from the array.
Parameters:
array : The array from which to remove and return the last element.
Returns the last element of the array before removal.
Example:
test {
let arr = [1, 2, 3]
inspect(arr.unsafe_pop(), content="3")
inspect(arr, content="[1, 2]")
}
unsafe_pop() |> fn[T] ignore(t : T) -> Unit
Evaluates an expression and discards its result. This is useful when you want
to execute an expression for its side effects but don't care about its return
value, or when you want to explicitly indicate that a value is intentionally
unused.
Parameters:
value : The value to be ignored. Can be of any type.
Example:
test {
let x = 42
ignore(x) // Explicitly ignore the value
let mut sum = 0
ignore([1, 2, 3].iter().each(x => sum = sum + x)) // Ignore the Unit return value of each()
}
ignore
}
这里唯一复杂的实现是 Thunk 的 evaluate. 这里我们需要先把这个 thunk 推到栈顶用于后面的依赖记录. node_stack 的定义如下:
let Array[&Node]
node_stack : type Array[T]
An Array is a collection of values that supports random access and can
grow in size.
Array[&trait Node {
is_dirty(Self) -> Bool
set_dirty(Self, Bool) -> Unit
incoming_edges(Self) -> Array[&Node]
outgoing_edges(Self) -> Array[&Node]
is_changed(Self) -> Bool
evaluate(Self) -> Unit
}
Node] = []
然后做真正的计算, 并且把计算得到的值和上一个值做比较以更新 self.is_changed. is_changed 会在后面帮助我们判断是否需要重新计算一个 thunk.
dirty 和 propagate 的实现几乎和上面的伪代码相同:
fn trait Node {
is_dirty(Self) -> Bool
set_dirty(Self, Bool) -> Unit
incoming_edges(Self) -> Array[&Node]
outgoing_edges(Self) -> Array[&Node]
is_changed(Self) -> Bool
evaluate(Self) -> Unit
}
&Node::fn Node::dirty(self : &Node) -> Unit
dirty(&Node
self : &trait Node {
is_dirty(Self) -> Bool
set_dirty(Self, Bool) -> Unit
incoming_edges(Self) -> Array[&Node]
outgoing_edges(Self) -> Array[&Node]
is_changed(Self) -> Bool
evaluate(Self) -> Unit
}
Node) -> Unit
Unit {
for &Node
dependent in &Node
self.fn Node::incoming_edges(&Node) -> Array[&Node]
incoming_edges() {
if fn not(x : Bool) -> Bool
Performs logical negation on a boolean value.
Parameters:
value : The boolean value to negate.
Returns the logical NOT of the input value: true if the input is false,
and false if the input is true.
Example:
test {
inspect(not(true), content="false")
inspect(not(false), content="true")
}
not(&Node
dependent.fn Node::is_dirty(&Node) -> Bool
is_dirty()) {
&Node
dependent.fn Node::set_dirty(&Node, Bool) -> Unit
set_dirty(true)
&Node
dependent.fn Node::dirty(self : &Node) -> Unit
dirty()
}
}
}
fn trait Node {
is_dirty(Self) -> Bool
set_dirty(Self, Bool) -> Unit
incoming_edges(Self) -> Array[&Node]
outgoing_edges(Self) -> Array[&Node]
is_changed(Self) -> Bool
evaluate(Self) -> Unit
}
&Node::fn Node::propagate(self : &Node) -> Unit
propagate(&Node
self : &trait Node {
is_dirty(Self) -> Bool
set_dirty(Self, Bool) -> Unit
incoming_edges(Self) -> Array[&Node]
outgoing_edges(Self) -> Array[&Node]
is_changed(Self) -> Bool
evaluate(Self) -> Unit
}
Node) -> Unit
Unit {
if &Node
self.fn Node::is_dirty(&Node) -> Bool
is_dirty() {
&Node
self.fn Node::set_dirty(&Node, Bool) -> Unit
set_dirty(false)
for &Node
dependency in &Node
self.fn Node::outgoing_edges(&Node) -> Array[&Node]
outgoing_edges() {
&Node
dependency.fn Node::propagate(self : &Node) -> Unit
propagate()
if &Node
dependency.fn Node::is_changed(&Node) -> Bool
is_changed() {
&Node
self.fn Node::outgoing_edges(&Node) -> Array[&Node]
outgoing_edges().fn[T] Array::clear(self : Array[T]) -> Unit
Clears the array, removing all values.
This method has no effect on the allocated capacity of the array, only setting the length to 0.
Example
test {
let v = [3, 4, 5]
v.clear()
assert_eq(v.length(), 0)
}
clear()
&Node
self.fn Node::evaluate(&Node) -> Unit
evaluate()
return
}
}
}
}
有了这些函数的帮助, 最主要的三个 API: Cell::get, Cell::set 和 Thunk::get 实现起来就比较简单了.
为了得到一个 cell 的值, 我们直接返回结构体的 value 字段即可. 但在此之前, 如果它是在一个 Thunk::get 中被调用的, 我们要先把他记录为依赖.
fn[A] struct Cell[A] {
mut is_dirty: Bool
mut value: A
mut is_changed: Bool
incoming_edges: Array[&Node]
}
Cell::fn[A] Cell::get(self : Cell[A]) -> A
get(Cell[A]
self : struct Cell[A] {
mut is_dirty: Bool
mut value: A
mut is_changed: Bool
incoming_edges: Array[&Node]
}
Cell[type parameter A
A]) -> type parameter A
A {
if let node_stack : Array[&Node]
node_stack.fn[A] Array::last(self : Array[A]) -> A?
Returns the last element of the array, or None if the array is empty.
Parameters:
array : The array to get the last element from.
Returns an optional value containing the last element of the array. The
result is None if the array is empty, or Some(x) where x is the last
element of the array.
Example:
test {
let arr = [1, 2, 3]
inspect(arr.last(), content="Some(3)")
let empty : Array[Int] = []
inspect(empty.last(), content="None")
}
last() is (&Node) -> &Node?
Some(&Node
target) {
&Node
target.fn Node::outgoing_edges(&Node) -> Array[&Node]
outgoing_edges().fn[T] Array::push(self : Array[T], value : T) -> Unit
Adds an element to the end of the array.
If the array is at capacity, it will be reallocated.
Example
test {
let v = []
v.push(3)
}
push(Cell[A]
self)
Cell[A]
self.Array[&Node]
incoming_edges.fn[T] Array::push(self : Array[T], value : T) -> Unit
Adds an element to the end of the array.
If the array is at capacity, it will be reallocated.
Example
test {
let v = []
v.push(3)
}
push(&Node
target)
}
Cell[A]
self.A
value
}
当我们更改一个 cell 的值时, 我们需要先确保 is_changed 和 dirty 这两个状态被正确地更新了, 再将它的每一个父依赖标记为过时.
fn[A : trait Eq {
equal(Self, Self) -> Bool
op_equal(Self, Self) -> Bool
not_equal(Self, Self) -> Bool
}
Trait for types whose elements can test for equality
Eq] struct Cell[A] {
mut is_dirty: Bool
mut value: A
mut is_changed: Bool
incoming_edges: Array[&Node]
}
Cell::fn[A : Eq] Cell::set(self : Cell[A], new_value : A) -> Unit
set(Cell[A]
self : struct Cell[A] {
mut is_dirty: Bool
mut value: A
mut is_changed: Bool
incoming_edges: Array[&Node]
}
Cell[type parameter A
A], A
new_value : type parameter A
A) -> Unit
Unit {
if Cell[A]
self.A
value (_ : A, _ : A) -> Bool
!= A
new_value {
Cell[A]
self.Bool
is_changed = true
Cell[A]
self.A
value = A
new_value
Cell[A]
self.fn[A] Node::set_dirty(self : Cell[A], new_dirty : Bool) -> Unit
set_dirty(true)
trait Node {
is_dirty(Self) -> Bool
set_dirty(Self, Bool) -> Unit
incoming_edges(Self) -> Array[&Node]
outgoing_edges(Self) -> Array[&Node]
is_changed(Self) -> Bool
evaluate(Self) -> Unit
}
&Node::fn Node::dirty(self : &Node) -> Unit
dirty(Cell[A]
self)
}
}
和 Cell::get 类似, 在实现 Thunk::get 时我们需要先将 self 记录为依赖. 之后我们模式匹配 self.value, 如果它是 None, 这意味着这是第一次用户尝试计算这个 thunk 地值, 我们可�以简单地直接计算它; 如果它是 Some, 我们需要使用 propagate 来确保我们只重新计算那些需要的 thunk.
fn[A : trait Eq {
equal(Self, Self) -> Bool
op_equal(Self, Self) -> Bool
not_equal(Self, Self) -> Bool
}
Trait for types whose elements can test for equality
Eq] struct Thunk[A] {
mut is_dirty: Bool
mut value: A?
mut is_changed: Bool
thunk: () -> A
incoming_edges: Array[&Node]
outgoing_edges: Array[&Node]
}
Thunk::fn[A : Eq] Thunk::get(self : Thunk[A]) -> A
get(Thunk[A]
self : struct Thunk[A] {
mut is_dirty: Bool
mut value: A?
mut is_changed: Bool
thunk: () -> A
incoming_edges: Array[&Node]
outgoing_edges: Array[&Node]
}
Thunk[type parameter A
A]) -> type parameter A
A {
if let node_stack : Array[&Node]
node_stack.fn[A] Array::last(self : Array[A]) -> A?
Returns the last element of the array, or None if the array is empty.
Parameters:
array : The array to get the last element from.
Returns an optional value containing the last element of the array. The
result is None if the array is empty, or Some(x) where x is the last
element of the array.
Example:
test {
let arr = [1, 2, 3]
inspect(arr.last(), content="Some(3)")
let empty : Array[Int] = []
inspect(empty.last(), content="None")
}
last() is (&Node) -> &Node?
Some(&Node
target) {
&Node
target.fn Node::outgoing_edges(&Node) -> Array[&Node]
outgoing_edges().fn[T] Array::push(self : Array[T], value : T) -> Unit
Adds an element to the end of the array.
If the array is at capacity, it will be reallocated.
Example
test {
let v = []
v.push(3)
}
push(Thunk[A]
self)
Thunk[A]
self.Array[&Node]
incoming_edges.fn[T] Array::push(self : Array[T], value : T) -> Unit
Adds an element to the end of the array.
If the array is at capacity, it will be reallocated.
Example
test {
let v = []
v.push(3)
}
push(&Node
target)
}
match Thunk[A]
self.A?
value {
A?
None => Thunk[A]
self.fn[A : Eq] Node::evaluate(self : Thunk[A]) -> Unit
evaluate()
(A) -> A?
Some(_) => trait Node {
is_dirty(Self) -> Bool
set_dirty(Self, Bool) -> Unit
incoming_edges(Self) -> Array[&Node]
outgoing_edges(Self) -> Array[&Node]
is_changed(Self) -> Bool
evaluate(Self) -> Unit
}
&Node::fn Node::propagate(self : &Node) -> Unit
propagate(Thunk[A]
self)
}
Thunk[A]
self.A?
value.fn[X] Option::unwrap(self : X?) -> X
Extract the value in Some.
If the value is None, it throws a panic.
unwrap()
}
参考
- Adapton: Composable, demand-driven incremental computation, PLDI 2014 adapton 的原论文
- illusory0x0/adapton.mbt adapton 库的 MoonBit 实现