在MoonBit中实现IntMap

键值对容器是现代编程语言必备的标准库成员之一,它应用广泛,所以其基本操作的性能非常重要。函数式语言的键值对容器实现大多基于某种平衡二叉搜索树,这样实现的键值对容器在查找和插入操作上表现优秀,但在需要合并两个键值对容器时表现不佳,命令式语言常用的哈希表也不擅长合并操作。
IntMap是一种为整数特化的不可变键值对容器,它只能以整数为键,通过牺牲一定的通用性,它实现了高效的合并/取交集操作。本文将从最朴素的二叉字典树开始,逐步改进到IntMap.
二叉字典树
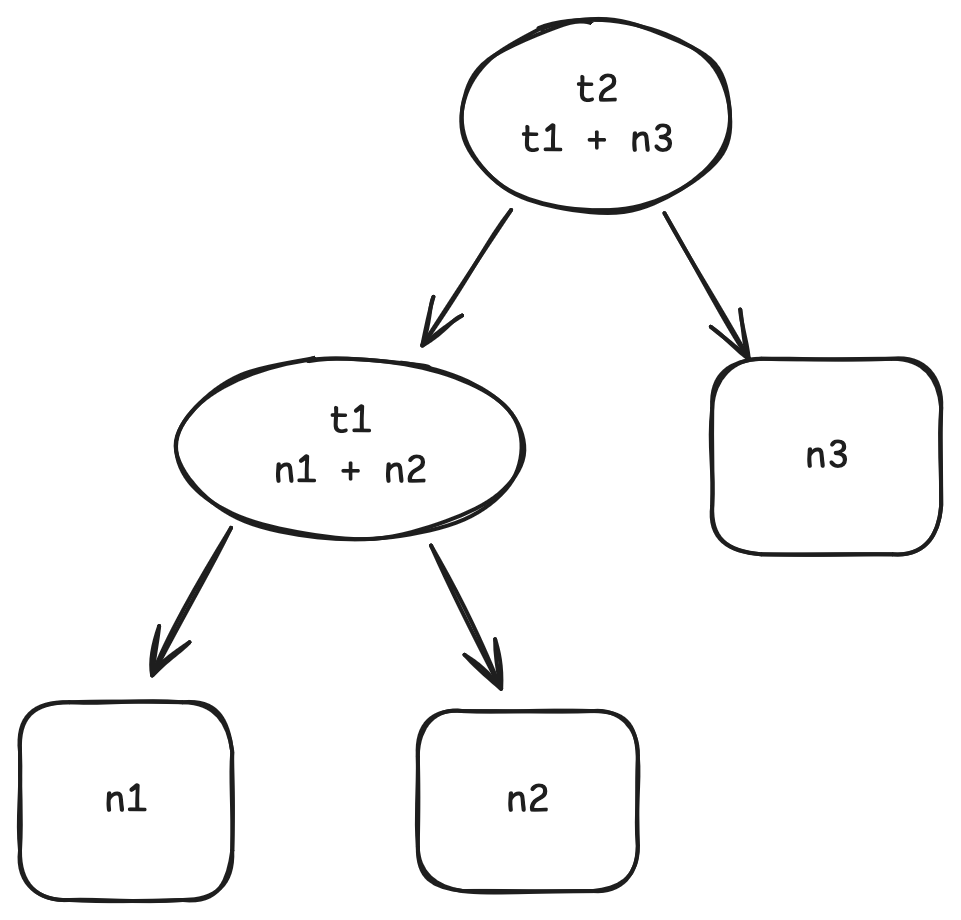
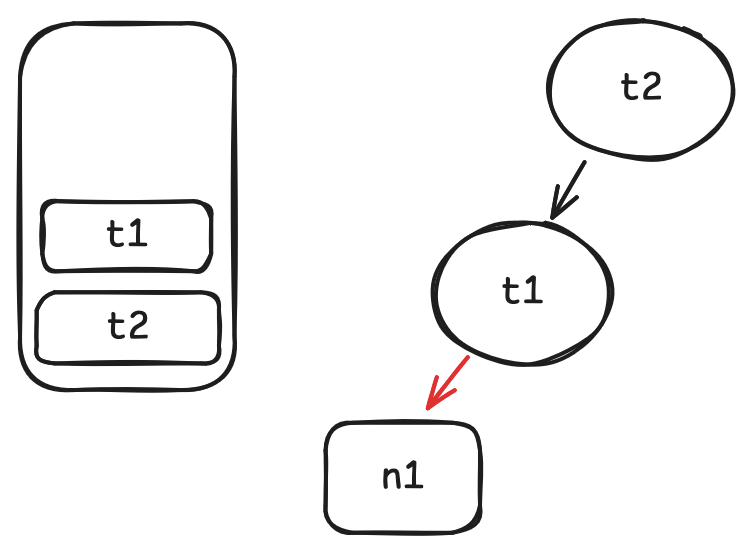
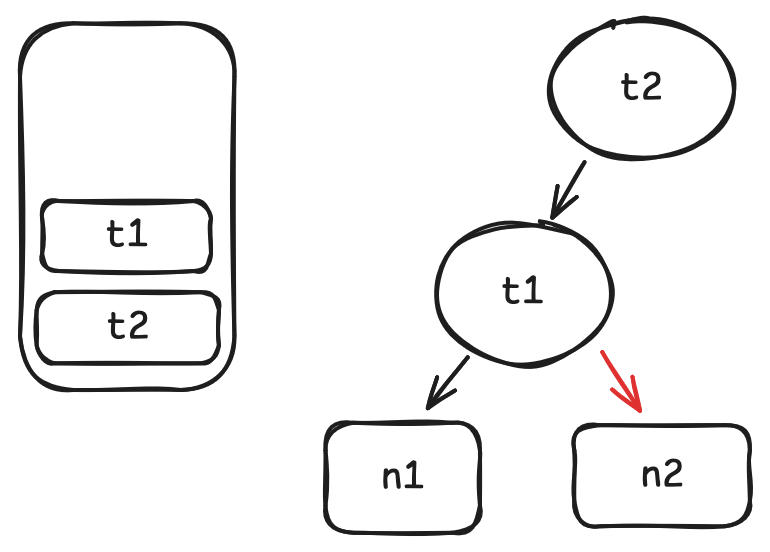
二叉字典树是一种使用每个键的二进制表示决定其位置的二叉树,键的二进制表示是一长串有限的0和1,那么假如当前位是0,就向左子树递归,当前位为1则向右子树递归.
///|
enum BinTrie[T] {
BinTrie[T]
Empty
(T) -> BinTrie[T]
Leaf(type parameter T
T)
(left~ : BinTrie[T], right~ : BinTrie[T]) -> BinTrie[T]
Branch(BinTrie[T]
left~ : enum BinTrie[T] {
Empty
Leaf(T)
Branch(left~ : BinTrie[T], right~ : BinTrie[T])
}
BinTrie[type parameter T
T], BinTrie[T]
right~ : enum BinTrie[T] {
Empty
Leaf(T)
Branch(left~ : BinTrie[T], right~ : BinTrie[T])
}
BinTrie[type parameter T
T])
}
要在二叉字典树里查找某个键对应的值,只需要依次读取键的二进制位,根据其值选择向左或者向右移动,直到到达某个叶子节点
此处读取二进制位的顺序是从整数最小位到最高位
fn[T] enum BinTrie[T] {
Empty
Leaf(T)
Branch(left~ : BinTrie[T], right~ : BinTrie[T])
}
BinTrie::fn[T] BinTrie::lookup(self : BinTrie[T], key : UInt) -> T?
lookup(BinTrie[T]
self : enum BinTrie[T] {
Empty
Leaf(T)
Branch(left~ : BinTrie[T], right~ : BinTrie[T])
}
BinTrie[type parameter T
T], UInt
key : UInt
UInt) -> type parameter T
T? {
match BinTrie[T]
self {
BinTrie[T]
Empty => T?
None
(T) -> BinTrie[T]
Leaf(T
value) => (T) -> T?
Some(T
value)
(left~ : BinTrie[T], right~ : BinTrie[T]) -> BinTrie[T]
Branch(BinTrie[T]
left~, BinTrie[T]
right~) =>
if UInt
key fn Mod::mod(self : UInt, other : UInt) -> UInt
Calculates the remainder of dividing one unsigned integer by another.
Parameters:
self : The unsigned integer dividend.other : The unsigned integer divisor.
Returns the remainder of the division operation.
Throws a panic if other is zero.
Example:
test {
let a = 17U
let b = 5U
inspect(a % b, content="2") // 17 divided by 5 gives quotient 3 and remainder 2
inspect(7U % 4U, content="3")
}
% 2U fn Eq::equal(self : UInt, other : UInt) -> Bool
Compares two unsigned 32-bit integers for equality.
Parameters:
self : The first unsigned integer operand.other : The second unsigned integer operand to compare with.
Returns true if both integers have the same value, false otherwise.
Example:
test {
let a = 42U
let b = 42U
let c = 24U
inspect(a == b, content="true")
inspect(a == c, content="false")
}
== 0 {
BinTrie[T]
left.fn[T] BinTrie::lookup(self : BinTrie[T], key : UInt) -> T?
lookup(UInt
key fn Div::div(self : UInt, other : UInt) -> UInt
Performs division between two unsigned 32-bit integers. The operation follows
standard unsigned integer division rules, where the result is truncated
towards zero.
Parameters:
self : The dividend (the number to be divided).other : The divisor (the number to divide by).
Returns an unsigned 32-bit integer representing the quotient of the division.
Example:
test {
let a = 42U
let b = 5U
inspect(a / b, content="8") // Using infix operator
}
/ 2)
} else {
BinTrie[T]
right.fn[T] BinTrie::lookup(self : BinTrie[T], key : UInt) -> T?
lookup(UInt
key fn Div::div(self : UInt, other : UInt) -> UInt
Performs division between two unsigned 32-bit integers. The operation follows
standard unsigned integer division rules, where the result is truncated
towards zero.
Parameters:
self : The dividend (the number to be divided).other : The divisor (the number to divide by).
Returns an unsigned 32-bit integer representing the quotient of the division.
Example:
test {
let a = 42U
let b = 5U
inspect(a / b, content="8") // Using infix operator
}
/ 2)
}
}
}
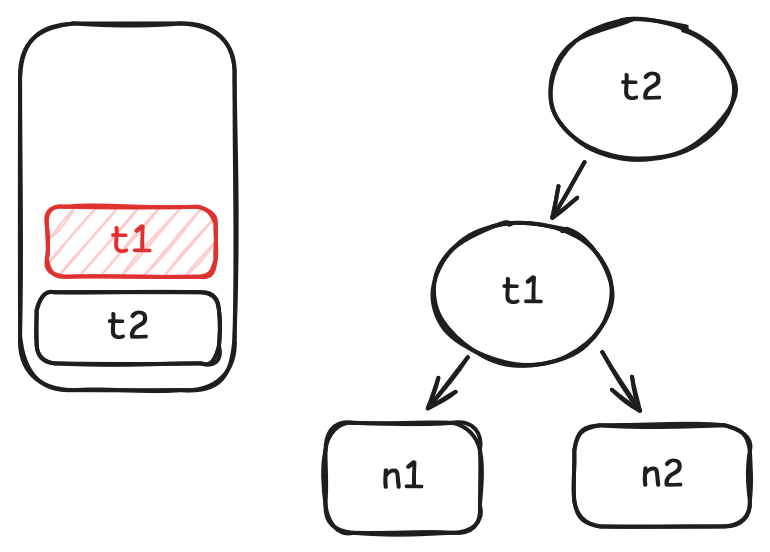
为了避免创建过多空树,我们不直接调用值构造子,而是使用branch方法
fn[T] enum BinTrie[T] {
Empty
Leaf(T)
Branch(left~ : BinTrie[T], right~ : BinTrie[T])
}
BinTrie::fn[T] BinTrie::br(left : BinTrie[T], right : BinTrie[T]) -> BinTrie[T]
br(BinTrie[T]
left : enum BinTrie[T] {
Empty
Leaf(T)
Branch(left~ : BinTrie[T], right~ : BinTrie[T])
}
BinTrie[type parameter T
T], BinTrie[T]
right : enum BinTrie[T] {
Empty
Leaf(T)
Branch(left~ : BinTrie[T], right~ : BinTrie[T])
}
BinTrie[type parameter T
T]) -> enum BinTrie[T] {
Empty
Leaf(T)
Branch(left~ : BinTrie[T], right~ : BinTrie[T])
}
BinTrie[type parameter T
T] {
match (BinTrie[T]
left, BinTrie[T]
right) {
(BinTrie[T]
Empty, BinTrie[T]
Empty) => BinTrie[T]
Empty
_ => (left~ : BinTrie[T], right~ : BinTrie[T]) -> BinTrie[T]
Branch(BinTrie[T]
left~, BinTrie[T]
right~)
}
}
Patricia Tree
Patricia Tree在二叉字典树的基础上保存了更多信息以加速查找,在每个分叉的地方,它都保留子树中所有键的公共前缀(虽然此处是从最低位开始计算,但我们仍然使用前缀�这种说法),并用一个无符号整数标记当前的分支位(branching bit).这样一来,查找时需要经过的分支数量大大减少。
///|
enum PatriciaTree[T] {
PatriciaTree[T]
Empty
(key~ : Int, value~ : T) -> PatriciaTree[T]
Leaf(Int
key~ : Int
Int, T
value~ : type parameter T
T)
(prefix~ : UInt, mask~ : UInt, left~ : PatriciaTree[T], right~ : PatriciaTree[T]) -> PatriciaTree[T]
Branch(
UInt
prefix~ : UInt
UInt,
UInt
mask~ : UInt
UInt,
PatriciaTree[T]
left~ : enum PatriciaTree[T] {
Empty
Leaf(key~ : Int, value~ : T)
Branch(prefix~ : UInt, mask~ : UInt, left~ : PatriciaTree[T], right~ : PatriciaTree[T])
}
PatriciaTree[type parameter T
T],
PatriciaTree[T]
right~ : enum PatriciaTree[T] {
Empty
Leaf(key~ : Int, value~ : T)
Branch(prefix~ : UInt, mask~ : UInt, left~ : PatriciaTree[T], right~ : PatriciaTree[T])
}
PatriciaTree[type parameter T
T]
)
}
///|
fn[T] enum PatriciaTree[T] {
Empty
Leaf(key~ : Int, value~ : T)
Branch(prefix~ : UInt, mask~ : UInt, left~ : PatriciaTree[T], right~ : PatriciaTree[T])
}
PatriciaTree::fn[T] PatriciaTree::lookup(self : PatriciaTree[T], key : Int) -> T?
lookup(PatriciaTree[T]
self : enum PatriciaTree[T] {
Empty
Leaf(key~ : Int, value~ : T)
Branch(prefix~ : UInt, mask~ : UInt, left~ : PatriciaTree[T], right~ : PatriciaTree[T])
}
PatriciaTree[type parameter T
T], Int
key : Int
Int) -> type parameter T
T? {
match PatriciaTree[T]
self {
PatriciaTree[T]
Empty => T?
None
(key~ : Int, value~ : T) -> PatriciaTree[T]
Leaf(Int
key=Int
k, T
value~) => if Int
k fn Eq::equal(self : Int, other : Int) -> Bool
Compares two integers for equality.
Parameters:
self : The first integer to compare.other : The second integer to compare.
Returns true if both integers have the same value, false otherwise.
Example:
test {
inspect(42 == 42, content="true")
inspect(42 == -42, content="false")
}
== Int
key { (T) -> T?
Some(T
value) } else { T?
None }
(prefix~ : UInt, mask~ : UInt, left~ : PatriciaTree[T], right~ : PatriciaTree[T]) -> PatriciaTree[T]
Branch(UInt
prefix~, UInt
mask~, PatriciaTree[T]
left~, PatriciaTree[T]
right~) =>
if Bool
!fn match_prefix(key~ : UInt, prefix~ : UInt, mask~ : UInt) -> Bool
match_prefixBool
(UInt
keyBool
=Int
keyBool
.fn Int::reinterpret_as_uint(self : Int) -> UInt
reinterpret the signed int as unsigned int, when the value is
non-negative, i.e, 0..=2^31-1, the value is the same. When the
value is negative, it turns into a large number,
for example, -1 turns into 2^32-1
reinterpret_as_uintBool
(), UInt
prefixBool
~, UInt
maskBool
~) {
T?
None
} else if fn zero(k : UInt, mask~ : UInt) -> Bool
zero(Int
key.fn Int::reinterpret_as_uint(self : Int) -> UInt
reinterpret the signed int as unsigned int, when the value is
non-negative, i.e, 0..=2^31-1, the value is the same. When the
value is negative, it turns into a large number,
for example, -1 turns into 2^32-1
reinterpret_as_uint(), UInt
mask~) {
PatriciaTree[T]
left.fn[T] PatriciaTree::lookup(self : PatriciaTree[T], key : Int) -> T?
lookup(Int
key)
} else {
PatriciaTree[T]
right.fn[T] PatriciaTree::lookup(self : PatriciaTree[T], key : Int) -> T?
lookup(Int
key)
}
}
}
///|
fn fn get_prefix(key : UInt, mask~ : UInt) -> UInt
get_prefix(UInt
key : UInt
UInt, UInt
mask~ : UInt
UInt) -> UInt
UInt {
UInt
key fn BitAnd::land(self : UInt, other : UInt) -> UInt
Performs a bitwise AND operation between two unsigned 32-bit integers. For
each bit position, the result is 1 if the bits at that position in both
operands are 1, and 0 otherwise.
Parameters:
self : The first unsigned 32-bit integer operand.other : The second unsigned 32-bit integer operand.
Returns an unsigned 32-bit integer representing the result of the bitwise AND
operation.
Example:
test {
let a = 0xF0F0U // 1111_0000_1111_0000
let b = 0xFF00U // 1111_1111_0000_0000
inspect(a & b, content="61440") // 1111_0000_0000_0000 = 61440
}
& (UInt
mask fn Sub::sub(self : UInt, other : UInt) -> UInt
Performs subtraction between two unsigned 32-bit integers. When the result
would be negative, the function wraps around using modular arithmetic (2^32).
Parameters:
self : The first unsigned 32-bit integer (minuend).other : The second unsigned 32-bit integer to subtract from the first
(subtrahend).
Returns a new unsigned 32-bit integer representing the difference between the
two numbers. If the result would be negative, it wraps around to a positive
number by adding 2^32 repeatedly until the result is in range.
Example:
test {
let a = 5U
let b = 3U
inspect(a - b, content="2")
let c = 3U
let d = 5U
inspect(c - d, content="4294967294") // wraps around to 2^32 - 2
}
- 1U)
}
///|
fn fn match_prefix(key~ : UInt, prefix~ : UInt, mask~ : UInt) -> Bool
match_prefix(UInt
key~ : UInt
UInt, UInt
prefix~ : UInt
UInt, UInt
mask~ : UInt
UInt) -> Bool
Bool {
fn get_prefix(key : UInt, mask~ : UInt) -> UInt
get_prefix(UInt
key, UInt
mask~) fn Eq::equal(self : UInt, other : UInt) -> Bool
Compares two unsigned 32-bit integers for equality.
Parameters:
self : The first unsigned integer operand.other : The second unsigned integer operand to compare with.
Returns true if both integers have the same value, false otherwise.
Example:
test {
let a = 42U
let b = 42U
let c = 24U
inspect(a == b, content="true")
inspect(a == c, content="false")
}
== UInt
prefix
}
///|
fn fn zero(k : UInt, mask~ : UInt) -> Bool
zero(UInt
k : UInt
UInt, UInt
mask~ : UInt
UInt) -> Bool
Bool {
(UInt
k fn BitAnd::land(self : UInt, other : UInt) -> UInt
Performs a bitwise AND operation between two unsigned 32-bit integers. For
each bit position, the result is 1 if the bits at that position in both
operands are 1, and 0 otherwise.
Parameters:
self : The first unsigned 32-bit integer operand.other : The second unsigned 32-bit integer operand.
Returns an unsigned 32-bit integer representing the result of the bitwise AND
operation.
Example:
test {
let a = 0xF0F0U // 1111_0000_1111_0000
let b = 0xFF00U // 1111_1111_0000_0000
inspect(a & b, content="61440") // 1111_0000_0000_0000 = 61440
}
& UInt
mask) fn Eq::equal(self : UInt, other : UInt) -> Bool
Compares two unsigned 32-bit integers for equality.
Parameters:
self : The first unsigned integer operand.other : The second unsigned integer operand to compare with.
Returns true if both integers have the same value, false otherwise.
Example:
test {
let a = 42U
let b = 42U
let c = 24U
inspect(a == b, content="true")
inspect(a == c, content="false")
}
== 0
}
现在branch方法可以做更多优化, 保证Branch节点的子树不含Empty.
///|
fn[T] enum PatriciaTree[T] {
Empty
Leaf(key~ : Int, value~ : T)
Branch(prefix~ : UInt, mask~ : UInt, left~ : PatriciaTree[T], right~ : PatriciaTree[T])
}
PatriciaTree::fn[T] PatriciaTree::branch(prefix~ : UInt, mask~ : UInt, left~ : PatriciaTree[T], right~ : PatriciaTree[T]) -> PatriciaTree[T]
branch(
UInt
prefix~ : UInt
UInt,
UInt
mask~ : UInt
UInt,
PatriciaTree[T]
left~ : enum PatriciaTree[T] {
Empty
Leaf(key~ : Int, value~ : T)
Branch(prefix~ : UInt, mask~ : UInt, left~ : PatriciaTree[T], right~ : PatriciaTree[T])
}
PatriciaTree[type parameter T
T],
PatriciaTree[T]
right~ : enum PatriciaTree[T] {
Empty
Leaf(key~ : Int, value~ : T)
Branch(prefix~ : UInt, mask~ : UInt, left~ : PatriciaTree[T], right~ : PatriciaTree[T])
}
PatriciaTree[type parameter T
T],
) -> enum PatriciaTree[T] {
Empty
Leaf(key~ : Int, value~ : T)
Branch(prefix~ : UInt, mask~ : UInt, left~ : PatriciaTree[T], right~ : PatriciaTree[T])
}
PatriciaTree[type parameter T
T] {
match (PatriciaTree[T]
left, PatriciaTree[T]
right) {
(PatriciaTree[T]
Empty, PatriciaTree[T]
right) => PatriciaTree[T]
right
(PatriciaTree[T]
left, PatriciaTree[T]
Empty) => PatriciaTree[T]
left
_ => (prefix~ : UInt, mask~ : UInt, left~ : PatriciaTree[T], right~ : PatriciaTree[T]) -> PatriciaTree[T]
Branch(UInt
prefix~, UInt
mask~, PatriciaTree[T]
left~, PatriciaTree[T]
right~)
}
}
插入与合并
既然类型定义已经确定,接下来要做的就是实现插入和合并操作。由于插入操作也可以看作将一个只有一个叶节点的树与原本的树合并,所以我们优先介绍合并操作的实现。
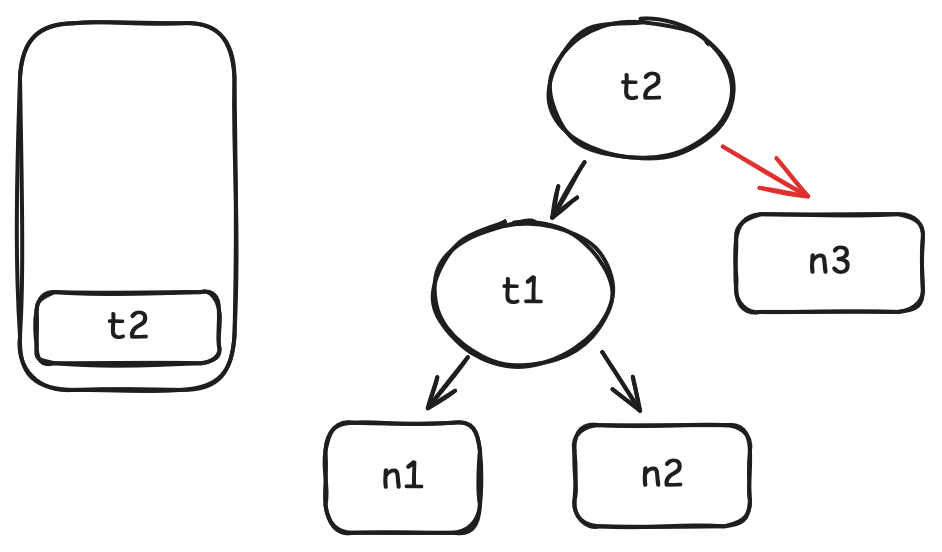
我们首先讨论可以走捷径的情况:假设我们有两个非空树t0和t1,它们的最长公共前缀分别为p0和p1且p0和p1互不包含, 那么不管t0和t1有多大,合并它们的成本都是一样的,因为只需要创建一个新的Branch节点。我们通过辅助函数join来实现。
生成掩码的函数gen_mask利用了整数二进制补码的一个特性来寻找最低的分支位。
假设输入x的二进制表示为
00100100000
那么,x.lnot()得到
11011011111
加一得到
11011100000
跟原来的x进行按位与后,得到:
00000100000
///|
fn[T] fn[T] join(p0 : UInt, t0 : PatriciaTree[T], p1 : UInt, t1 : PatriciaTree[T]) -> PatriciaTree[T]
join(
UInt
p0 : UInt
UInt,
PatriciaTree[T]
t0 : enum PatriciaTree[T] {
Empty
Leaf(key~ : Int, value~ : T)
Branch(prefix~ : UInt, mask~ : UInt, left~ : PatriciaTree[T], right~ : PatriciaTree[T])
}
PatriciaTree[type parameter T
T],
UInt
p1 : UInt
UInt,
PatriciaTree[T]
t1 : enum PatriciaTree[T] {
Empty
Leaf(key~ : Int, value~ : T)
Branch(prefix~ : UInt, mask~ : UInt, left~ : PatriciaTree[T], right~ : PatriciaTree[T])
}
PatriciaTree[type parameter T
T],
) -> enum PatriciaTree[T] {
Empty
Leaf(key~ : Int, value~ : T)
Branch(prefix~ : UInt, mask~ : UInt, left~ : PatriciaTree[T], right~ : PatriciaTree[T])
}
PatriciaTree[type parameter T
T] {
let UInt
mask = fn gen_mask(p0 : UInt, p1 : UInt) -> UInt
gen_mask(UInt
p0, UInt
p1)
if fn zero(k : UInt, mask~ : UInt) -> Bool
zero(UInt
p0, UInt
mask~) {
PatriciaTree::(prefix~ : UInt, mask~ : UInt, left~ : PatriciaTree[T], right~ : PatriciaTree[T]) -> PatriciaTree[T]
Branch(UInt
prefix=fn get_prefix(key : UInt, mask~ : UInt) -> UInt
get_prefix(UInt
p0, UInt
mask~), UInt
mask~, PatriciaTree[T]
left=PatriciaTree[T]
t0, PatriciaTree[T]
right=PatriciaTree[T]
t1)
} else {
PatriciaTree::(prefix~ : UInt, mask~ : UInt, left~ : PatriciaTree[T], right~ : PatriciaTree[T]) -> PatriciaTree[T]
Branch(UInt
prefix=fn get_prefix(key : UInt, mask~ : UInt) -> UInt
get_prefix(UInt
p0, UInt
mask~), UInt
mask~, PatriciaTree[T]
left=PatriciaTree[T]
t1, PatriciaTree[T]
right=PatriciaTree[T]
t0)
}
}
///|
fn fn gen_mask(p0 : UInt, p1 : UInt) -> UInt
gen_mask(UInt
p0 : UInt
UInt, UInt
p1 : UInt
UInt) -> UInt
UInt {
fn (UInt) -> UInt
lowest_bit(UInt
x : UInt
UInt) -> UInt
UInt {
UInt
x fn BitAnd::land(self : UInt, other : UInt) -> UInt
Performs a bitwise AND operation between two unsigned 32-bit integers. For
each bit position, the result is 1 if the bits at that position in both
operands are 1, and 0 otherwise.
Parameters:
self : The first unsigned 32-bit integer operand.other : The second unsigned 32-bit integer operand.
Returns an unsigned 32-bit integer representing the result of the bitwise AND
operation.
Example:
test {
let a = 0xF0F0U // 1111_0000_1111_0000
let b = 0xFF00U // 1111_1111_0000_0000
inspect(a & b, content="61440") // 1111_0000_0000_0000 = 61440
}
& (UInt
x.fn UInt::reinterpret_as_int(self : UInt) -> Int
reinterpret the unsigned int as signed int
For number within the range of 0..=2^31-1,
the value is the same. For number within the range of 2^31..=2^32-1,
the value is negative
reinterpret_as_int().fn Neg::neg(self : Int) -> Int
Performs arithmetic negation on an integer value, returning its additive
inverse.
Parameters:
self : The integer value to negate.
Returns the negation of the input value. For all inputs except
Int::min_value(), returns the value with opposite sign. When the input is
Int::min_value(), returns Int::min_value() due to two's complement
representation.
Example:
test {
inspect(-42, content="-42")
inspect(42, content="42")
inspect(2147483647, content="2147483647") // negating near min value
}
neg().fn Int::reinterpret_as_uint(self : Int) -> UInt
reinterpret the signed int as unsigned int, when the value is
non-negative, i.e, 0..=2^31-1, the value is the same. When the
value is negative, it turns into a large number,
for example, -1 turns into 2^32-1
reinterpret_as_uint())
}
(UInt) -> UInt
lowest_bit(UInt
p0 fn BitXOr::lxor(self : UInt, other : UInt) -> UInt
Performs a bitwise XOR (exclusive OR) operation between two unsigned 32-bit
integers. Each bit in the result is set to 1 if the corresponding bits in the
operands are different, and 0 if they are the same.
Parameters:
self : The first unsigned 32-bit integer operand.other : The second unsigned 32-bit integer operand.
Returns the result of the bitwise XOR operation.
Example:
test {
let a = 0xFF00U // Binary: 1111_1111_0000_0000
let b = 0x0F0FU // Binary: 0000_1111_0000_1111
inspect(a ^ b, content="61455") // Binary: 1111_0000_0000_1111
}
^ UInt
p1)
}
万事俱备,现在可以开始编写insert_with函数了。对Empty和Leaf分支的处理都非常直接,而对于Branch, 在前缀互不包含时调用join,其他情况则根据分支位选择一个分支递归下去。
///|
fn[T] enum PatriciaTree[T] {
Empty
Leaf(key~ : Int, value~ : T)
Branch(prefix~ : UInt, mask~ : UInt, left~ : PatriciaTree[T], right~ : PatriciaTree[T])
}
PatriciaTree::fn[T] PatriciaTree::insert_with(self : PatriciaTree[T], k : Int, v : T, combine~ : (T, T) -> T) -> PatriciaTree[T]
insert_with(
PatriciaTree[T]
self : enum PatriciaTree[T] {
Empty
Leaf(key~ : Int, value~ : T)
Branch(prefix~ : UInt, mask~ : UInt, left~ : PatriciaTree[T], right~ : PatriciaTree[T])
}
PatriciaTree[type parameter T
T],
Int
k : Int
Int,
T
v : type parameter T
T,
(T, T) -> T
combine~ : (type parameter T
T, type parameter T
T) -> type parameter T
T,
) -> enum PatriciaTree[T] {
Empty
Leaf(key~ : Int, value~ : T)
Branch(prefix~ : UInt, mask~ : UInt, left~ : PatriciaTree[T], right~ : PatriciaTree[T])
}
PatriciaTree[type parameter T
T] {
fn (PatriciaTree[T]) -> PatriciaTree[T]
go(PatriciaTree[T]
tree : enum PatriciaTree[T] {
Empty
Leaf(key~ : Int, value~ : T)
Branch(prefix~ : UInt, mask~ : UInt, left~ : PatriciaTree[T], right~ : PatriciaTree[T])
}
PatriciaTree[type parameter T
T]) -> enum PatriciaTree[T] {
Empty
Leaf(key~ : Int, value~ : T)
Branch(prefix~ : UInt, mask~ : UInt, left~ : PatriciaTree[T], right~ : PatriciaTree[T])
}
PatriciaTree[type parameter T
T] {
match PatriciaTree[T]
tree {
PatriciaTree[T]
Empty => (key~ : Int, value~ : T) -> PatriciaTree[T]
Leaf(Int
key=Int
k, T
value=T
v)
(key~ : Int, value~ : T) -> PatriciaTree[T]
LeafPatriciaTree[T]
(Int
keyPatriciaTree[T]
~, T
valuePatriciaTree[T]
~) as tree =>
if Int
key fn Eq::equal(self : Int, other : Int) -> Bool
Compares two integers for equality.
Parameters:
self : The first integer to compare.other : The second integer to compare.
Returns true if both integers have the same value, false otherwise.
Example:
test {
inspect(42 == 42, content="true")
inspect(42 == -42, content="false")
}
== Int
k {
PatriciaTree::(key~ : Int, value~ : T) -> PatriciaTree[T]
Leaf(Int
key~, T
value=(T, T) -> T
combine(T
v, T
value))
} else {
fn[T] join(p0 : UInt, t0 : PatriciaTree[T], p1 : UInt, t1 : PatriciaTree[T]) -> PatriciaTree[T]
join(
Int
k.fn Int::reinterpret_as_uint(self : Int) -> UInt
reinterpret the signed int as unsigned int, when the value is
non-negative, i.e, 0..=2^31-1, the value is the same. When the
value is negative, it turns into a large number,
for example, -1 turns into 2^32-1
reinterpret_as_uint(),
(key~ : Int, value~ : T) -> PatriciaTree[T]
Leaf(Int
key=Int
k, T
value=T
v),
Int
key.fn Int::reinterpret_as_uint(self : Int) -> UInt
reinterpret the signed int as unsigned int, when the value is
non-negative, i.e, 0..=2^31-1, the value is the same. When the
value is negative, it turns into a large number,
for example, -1 turns into 2^32-1
reinterpret_as_uint(),
PatriciaTree[T]
tree,
)
}
(prefix~ : UInt, mask~ : UInt, left~ : PatriciaTree[T], right~ : PatriciaTree[T]) -> PatriciaTree[T]
BranchPatriciaTree[T]
(UInt
prefixPatriciaTree[T]
~, UInt
maskPatriciaTree[T]
~, PatriciaTree[T]
leftPatriciaTree[T]
~, PatriciaTree[T]
rightPatriciaTree[T]
~) as tree =>
if fn match_prefix(key~ : UInt, prefix~ : UInt, mask~ : UInt) -> Bool
match_prefix(UInt
key=Int
k.fn Int::reinterpret_as_uint(self : Int) -> UInt
reinterpret the signed int as unsigned int, when the value is
non-negative, i.e, 0..=2^31-1, the value is the same. When the
value is negative, it turns into a large number,
for example, -1 turns into 2^32-1
reinterpret_as_uint(), UInt
prefix~, UInt
mask~) {
if fn zero(k : UInt, mask~ : UInt) -> Bool
zero(Int
k.fn Int::reinterpret_as_uint(self : Int) -> UInt
reinterpret the signed int as unsigned int, when the value is
non-negative, i.e, 0..=2^31-1, the value is the same. When the
value is negative, it turns into a large number,
for example, -1 turns into 2^32-1
reinterpret_as_uint(), UInt
mask~) {
PatriciaTree::(prefix~ : UInt, mask~ : UInt, left~ : PatriciaTree[T], right~ : PatriciaTree[T]) -> PatriciaTree[T]
Branch(UInt
prefix~, UInt
mask~, PatriciaTree[T]
left=(PatriciaTree[T]) -> PatriciaTree[T]
go(PatriciaTree[T]
left), PatriciaTree[T]
right~)
} else {
PatriciaTree::(prefix~ : UInt, mask~ : UInt, left~ : PatriciaTree[T], right~ : PatriciaTree[T]) -> PatriciaTree[T]
Branch(UInt
prefix~, UInt
mask~, PatriciaTree[T]
left~, PatriciaTree[T]
right=(PatriciaTree[T]) -> PatriciaTree[T]
go(PatriciaTree[T]
right))
}
} else {
fn[T] join(p0 : UInt, t0 : PatriciaTree[T], p1 : UInt, t1 : PatriciaTree[T]) -> PatriciaTree[T]
join(Int
k.fn Int::reinterpret_as_uint(self : Int) -> UInt
reinterpret the signed int as unsigned int, when the value is
non-negative, i.e, 0..=2^31-1, the value is the same. When the
value is negative, it turns into a large number,
for example, -1 turns into 2^32-1
reinterpret_as_uint(), (key~ : Int, value~ : T) -> PatriciaTree[T]
Leaf(Int
key=Int
k, T
value=T
v), UInt
prefix, PatriciaTree[T]
tree)
}
}
}
(PatriciaTree[T]) -> PatriciaTree[T]
go(PatriciaTree[T]
self)
}
合并操作基本遵循相同的逻辑,略有不同的是它还要考虑前缀与掩码完全相同的情况。
///|
fn[T] enum PatriciaTree[T] {
Empty
Leaf(key~ : Int, value~ : T)
Branch(prefix~ : UInt, mask~ : UInt, left~ : PatriciaTree[T], right~ : PatriciaTree[T])
}
PatriciaTree::fn[T] PatriciaTree::union_with(combine~ : (T, T) -> T, left : PatriciaTree[T], right : PatriciaTree[T]) -> PatriciaTree[T]
union_with(
(T, T) -> T
combine~ : (type parameter T
T, type parameter T
T) -> type parameter T
T,
PatriciaTree[T]
left : enum PatriciaTree[T] {
Empty
Leaf(key~ : Int, value~ : T)
Branch(prefix~ : UInt, mask~ : UInt, left~ : PatriciaTree[T], right~ : PatriciaTree[T])
}
PatriciaTree[type parameter T
T],
PatriciaTree[T]
right : enum PatriciaTree[T] {
Empty
Leaf(key~ : Int, value~ : T)
Branch(prefix~ : UInt, mask~ : UInt, left~ : PatriciaTree[T], right~ : PatriciaTree[T])
}
PatriciaTree[type parameter T
T],
) -> enum PatriciaTree[T] {
Empty
Leaf(key~ : Int, value~ : T)
Branch(prefix~ : UInt, mask~ : UInt, left~ : PatriciaTree[T], right~ : PatriciaTree[T])
}
PatriciaTree[type parameter T
T] {
fn (PatriciaTree[T], PatriciaTree[T]) -> PatriciaTree[T]
go(PatriciaTree[T]
left : enum PatriciaTree[T] {
Empty
Leaf(key~ : Int, value~ : T)
Branch(prefix~ : UInt, mask~ : UInt, left~ : PatriciaTree[T], right~ : PatriciaTree[T])
}
PatriciaTree[type parameter T
T], PatriciaTree[T]
right : enum PatriciaTree[T] {
Empty
Leaf(key~ : Int, value~ : T)
Branch(prefix~ : UInt, mask~ : UInt, left~ : PatriciaTree[T], right~ : PatriciaTree[T])
}
PatriciaTree[type parameter T
T]) -> enum PatriciaTree[T] {
Empty
Leaf(key~ : Int, value~ : T)
Branch(prefix~ : UInt, mask~ : UInt, left~ : PatriciaTree[T], right~ : PatriciaTree[T])
}
PatriciaTree[type parameter T
T] {
match (PatriciaTree[T]
left, PatriciaTree[T]
right) {
(PatriciaTree[T]
Empty, PatriciaTree[T]
t) | (PatriciaTree[T]
t, PatriciaTree[T]
Empty) => PatriciaTree[T]
t
((key~ : Int, value~ : T) -> PatriciaTree[T]
Leaf(Int
key~, T
value~), PatriciaTree[T]
t) => PatriciaTree[T]
t.fn[T] PatriciaTree::insert_with(self : PatriciaTree[T], k : Int, v : T, combine~ : (T, T) -> T) -> PatriciaTree[T]
insert_with(Int
key, T
value, (T, T) -> T
combine~)
(PatriciaTree[T]
t, (key~ : Int, value~ : T) -> PatriciaTree[T]
Leaf(Int
key~, T
value~)) =>
PatriciaTree[T]
t.fn[T] PatriciaTree::insert_with(self : PatriciaTree[T], k : Int, v : T, combine~ : (T, T) -> T) -> PatriciaTree[T]
insert_with(Int
key, T
value, (T, T) -> T
combine=fn(T
x, T
y) { (T, T) -> T
combine(T
y, T
x) })
(
(prefix~ : UInt, mask~ : UInt, left~ : PatriciaTree[T], right~ : PatriciaTree[T]) -> PatriciaTree[T]
BranchPatriciaTree[T]
(UInt
prefixPatriciaTree[T]
=UInt
pPatriciaTree[T]
, UInt
maskPatriciaTree[T]
=UInt
mPatriciaTree[T]
, PatriciaTree[T]
leftPatriciaTree[T]
=PatriciaTree[T]
s0PatriciaTree[T]
, PatriciaTree[T]
rightPatriciaTree[T]
=PatriciaTree[T]
s1PatriciaTree[T]
) as s,
(prefix~ : UInt, mask~ : UInt, left~ : PatriciaTree[T], right~ : PatriciaTree[T]) -> PatriciaTree[T]
BranchPatriciaTree[T]
(UInt
prefixPatriciaTree[T]
=UInt
qPatriciaTree[T]
, UInt
maskPatriciaTree[T]
=UInt
nPatriciaTree[T]
, PatriciaTree[T]
leftPatriciaTree[T]
=PatriciaTree[T]
t0PatriciaTree[T]
, PatriciaTree[T]
rightPatriciaTree[T]
=PatriciaTree[T]
t1PatriciaTree[T]
) as t,
) =>
if UInt
m fn Eq::equal(self : UInt, other : UInt) -> Bool
Compares two unsigned 32-bit integers for equality.
Parameters:
self : The first unsigned integer operand.other : The second unsigned integer operand to compare with.
Returns true if both integers have the same value, false otherwise.
Example:
test {
let a = 42U
let b = 42U
let c = 24U
inspect(a == b, content="true")
inspect(a == c, content="false")
}
== UInt
n (Bool, Bool) -> Bool
&& UInt
p fn Eq::equal(self : UInt, other : UInt) -> Bool
Compares two unsigned 32-bit integers for equality.
Parameters:
self : The first unsigned integer operand.other : The second unsigned integer operand to compare with.
Returns true if both integers have the same value, false otherwise.
Example:
test {
let a = 42U
let b = 42U
let c = 24U
inspect(a == b, content="true")
inspect(a == c, content="false")
}
== UInt
q {
// The trees have the same prefix. Merge the subtrees
PatriciaTree::(prefix~ : UInt, mask~ : UInt, left~ : PatriciaTree[T], right~ : PatriciaTree[T]) -> PatriciaTree[T]
Branch(
UInt
prefix=UInt
p,
UInt
mask=UInt
m,
PatriciaTree[T]
left=(PatriciaTree[T], PatriciaTree[T]) -> PatriciaTree[T]
go(PatriciaTree[T]
s0, PatriciaTree[T]
t0),
PatriciaTree[T]
right=(PatriciaTree[T], PatriciaTree[T]) -> PatriciaTree[T]
go(PatriciaTree[T]
s1, PatriciaTree[T]
t1),
)
} else if UInt
m fn Compare::op_lt(x : UInt, y : UInt) -> Bool
< UInt
n (Bool, Bool) -> Bool
&& fn match_prefix(key~ : UInt, prefix~ : UInt, mask~ : UInt) -> Bool
match_prefix(UInt
key=UInt
q, UInt
prefix=UInt
p, UInt
mask=UInt
m) {
// q contains p. Merge t with a subtree of s
if fn zero(k : UInt, mask~ : UInt) -> Bool
zero(UInt
q, UInt
mask=UInt
m) {
(prefix~ : UInt, mask~ : UInt, left~ : PatriciaTree[T], right~ : PatriciaTree[T]) -> PatriciaTree[T]
Branch(UInt
prefix=UInt
p, UInt
mask=UInt
m, PatriciaTree[T]
left=(PatriciaTree[T], PatriciaTree[T]) -> PatriciaTree[T]
go(PatriciaTree[T]
s0, PatriciaTree[T]
t), PatriciaTree[T]
right=PatriciaTree[T]
s1)
} else {
(prefix~ : UInt, mask~ : UInt, left~ : PatriciaTree[T], right~ : PatriciaTree[T]) -> PatriciaTree[T]
Branch(UInt
prefix=UInt
p, UInt
mask=UInt
m, PatriciaTree[T]
left=PatriciaTree[T]
s0, PatriciaTree[T]
right=(PatriciaTree[T], PatriciaTree[T]) -> PatriciaTree[T]
go(PatriciaTree[T]
s1, PatriciaTree[T]
t))
}
} else if UInt
m fn Compare::op_gt(x : UInt, y : UInt) -> Bool
> UInt
n (Bool, Bool) -> Bool
&& fn match_prefix(key~ : UInt, prefix~ : UInt, mask~ : UInt) -> Bool
match_prefix(UInt
key=UInt
p, UInt
prefix=UInt
q, UInt
mask=UInt
n) {
// p contains q. Merge s with a subtree of t.
if fn zero(k : UInt, mask~ : UInt) -> Bool
zero(UInt
p, UInt
mask=UInt
n) {
(prefix~ : UInt, mask~ : UInt, left~ : PatriciaTree[T], right~ : PatriciaTree[T]) -> PatriciaTree[T]
Branch(UInt
prefix=UInt
q, UInt
mask=UInt
n, PatriciaTree[T]
left=(PatriciaTree[T], PatriciaTree[T]) -> PatriciaTree[T]
go(PatriciaTree[T]
s, PatriciaTree[T]
t0), PatriciaTree[T]
right=PatriciaTree[T]
t1)
} else {
(prefix~ : UInt, mask~ : UInt, left~ : PatriciaTree[T], right~ : PatriciaTree[T]) -> PatriciaTree[T]
Branch(UInt
prefix=UInt
q, UInt
mask=UInt
n, PatriciaTree[T]
left=PatriciaTree[T]
t0, PatriciaTree[T]
right=(PatriciaTree[T], PatriciaTree[T]) -> PatriciaTree[T]
go(PatriciaTree[T]
s, PatriciaTree[T]
t1))
}
} else {
fn[T] join(p0 : UInt, t0 : PatriciaTree[T], p1 : UInt, t1 : PatriciaTree[T]) -> PatriciaTree[T]
join(UInt
p, PatriciaTree[T]
s, UInt
q, PatriciaTree[T]
t)
}
}
}
(PatriciaTree[T], PatriciaTree[T]) -> PatriciaTree[T]
go(PatriciaTree[T]
left, PatriciaTree[T]
right)
}
Big-endian Patricia Tree
Big-endian Patricia Tree在Patricia Tree的基础上将计算分支位的顺序改成了从最高位到最低位,
这样做有什么好处呢?
-
更好的局部性。在Big-endian Patricia Tree中,大小相近的整数键会被放在邻近的地方。
-
便于高效地按顺序遍历键,只要普通地��实现前序/后序遍历即可。
-
常见情况下合并速度更快。在实践中,intmap里的整数键一般是连续的,这种情况下Big-endian Patricia Tree会有更长的公共前缀,让合并操作更快。
-
在Big-endian Patricia Tree中,如果把键看作无符号整数,右子树的每个键都大于当前节点的键(反过来,左子树是小于)。在编写查找函数时,只要使用无符号整数的比较就可判断接下来往哪个分支走,在大多数机器上这只需要一条指令即可完成,成本较低。
由于最终版本IntMap的实现与前文所述的Little Endian Patricia Tree相差不大,此处不再赘述,有需要的读者可以参考此仓库中的实现:https://github.com/moonbit-community/intmap
原实现中的一处错误
虽然IntMap的实现思路相当简洁明了,但在编写具体的实现代码时还是可能犯一些非常隐蔽的错误,甚至原论文作者在编写IntMap的SML实现时也未能幸免,后来又被OCaml的Ptset/Ptmap模块继承,直到2018年发表的QuickChecking Patricia Trees一文中这个问题才被发现。
具体来说,由于SML和OCaml语言没有提供无符号整数类型,在这两种语言的实现中IntMap类型里的掩码都通过int存储,但在union_with函数中对掩码进行比较时,他们都忘记了应该使用无符号整数的比较。